The Ultra Strategy: An Examination of Apple’s Adventurous Watch (Above Avalon Report)
An examination of the Apple Watch Ultra.
Written by Neil Cybart - December 21st, 2023
In 2022, Apple unveiled an all-new Apple Watch model designed for the adventurous. While previous Apple Watches were able to be used in extreme conditions, this model would be marketed as taking things to another level. A year after its unveiling, Apple Watch Ultra remains the most intriguing Apple Watch model as momentum flows to more capable devices worn on the wrist.
Table of Contents
Apple Watch History
Watch Line Expansion
The Ultra Unveiling
Bad (Initial) Reviews
The Strategy
Differentiation Details
Sales Implications
Future
An Above Avalon membership is required to read this report. Members can read the full report here. (Members: Reports are accessible via the archive. If you haven’t logged into the archive before, fill out this form to receive an invite.)
Payment is hosted by MoonClerk and secured by Stripe. Apple Pay and other mobile payment options are accepted. After signup, use this link to update your payment information and membership status at any time.
An audio version of this report is available to members who have the podcast add-on attached to their membership. More information about the podcast add-on is found here. Special Inside Orchard bundle pricing is available for Above Avalon members. Additional membership customization is available via the Financial Models add-on.
Apple Has a Decade-Long Lead in Wearables
Last week, Apple quietly unveiled one of the more remarkable pieces of technology that has been developed in the past few years. AssistiveTouch allows one to control an Apple Watch without actually touching the device. Instead, a series of hand and finger gestures can be used to control everything from answering a call to ending a workout. The video below showcasing AssistiveTouch is quite impressive:
Just two months prior, Facebook went on a big PR push to show the world how it was in early R&D stages of working on technology that can also use hand and finger movements to control future gadgets. AssistiveTouch is just the latest example of how Apple’s lead in wearables is still being underestimated. The evidence points to Apple having a wearables lead of not just a few years but more like a decade.
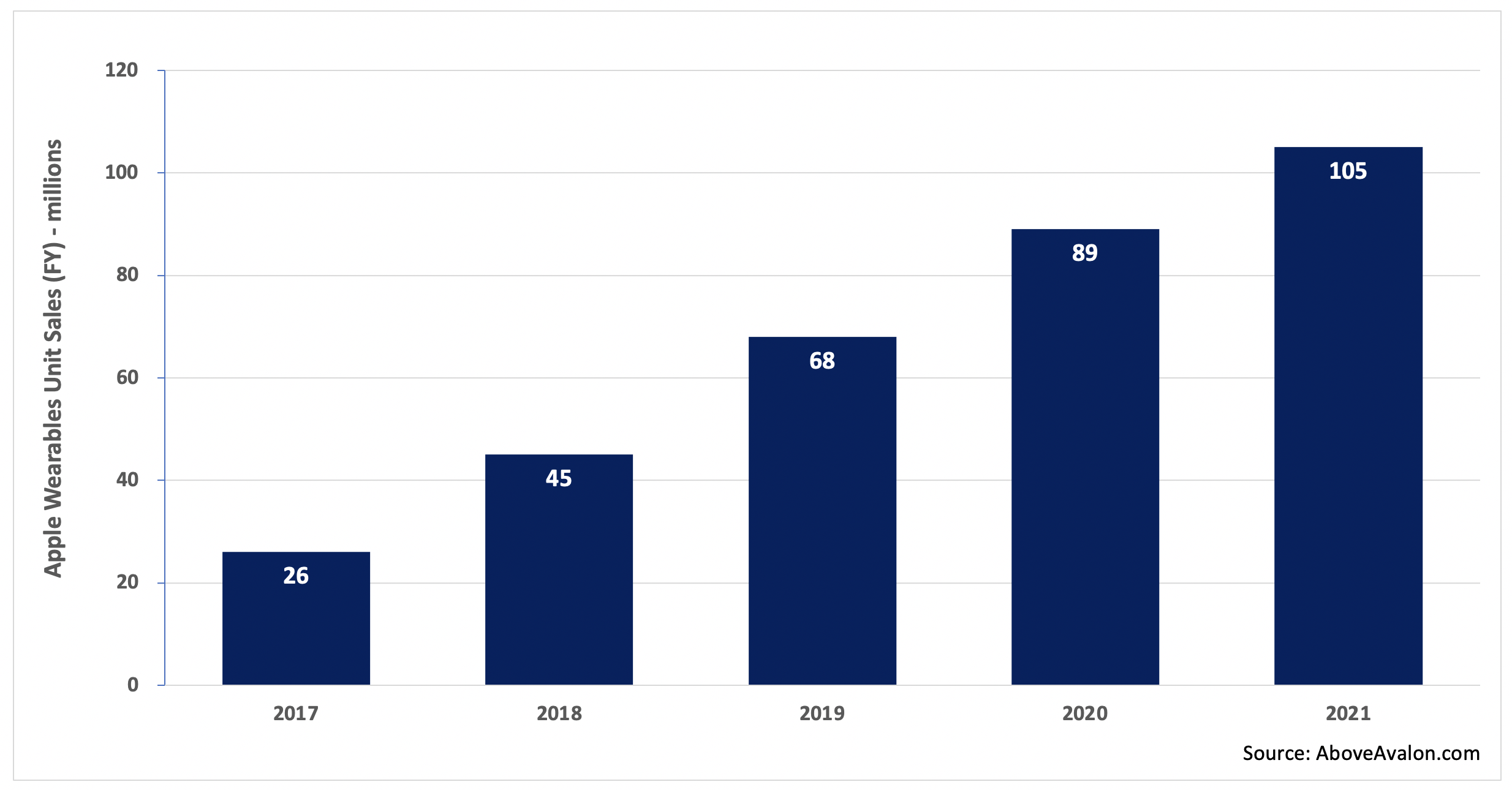
Apple Wearables by the Numbers
According to my estimate, Apple is on track to sell more than 100 million wearable devices in 2021. That total represents nearly 40% of the number of iPhones that will be sold during the same time period. Unit sales don’t tell the full story, however. On a new-user basis, Apple is seeing more people enter the wearables arena than buy a new iPhone for the first time.
Exhibit 1: Apple Wearables Unit Sales (2017 to 2021)
Note: Apple wearables include Apple Watch, AirPods, and select Beats headphones.
On a revenue basis, Apple Watch, AirPods, and select Beats headphones are a $30 billion per year business. That would rank Apple wearables on a combined basis just shy of a Fortune 100 company. Assuming continued Apple Watch and AirPods momentum, along with Apple expanding its wearables platform by getting into face wearables (AR/VR headsets and glasses), Apple wearables will likely be able to generate up to $50 billion of revenue annually within a few years.
Exhibit 2: Apple Wearables Revenue (2017 to 2021)
Note: Apple wearables include Apple Watch, AirPods, and select Beats headphones.
Measuring Apple’s Lead
When Apple unveiled the iPhone in January 2007, Steve Jobs famously said that the iPhone was “literally five years ahead of any other mobile phone.” He ended up being mostly correct. It took the competition a number of years, and a whole lot of copying, to catch up with what Apple had just unveiled.
With wearables, my suspicion is Apple’s lead is longer than five years. There are three components to Apple’s wearables lead:
Custom silicon / technology / sensors (a four to five-year lead over the competition, and that is being generous to the competition)
Design-led product development processes that emphasizes the user experience (adds three years to Apple’s lead)
A broader ecosystem build-out in terms of a suite of wearables and services (adds two years to Apple’s lead)
Apple has at least a four-to-five year lead over the competition when thinking about just the technology powering its wearables. Everything from custom silicon and health monitoring sensors to audio and AR-focused technologies come together to set Apple apart from the competition. Only a select number of companies will likely be able to even compete with Apple on the technology front. Others will be forced to pursue partnerships.
Apple’s wearables lead extends beyond four to five years when taking into account attributes that set wearables apart from mobile devices. Succeeding on the technology front is not enough. Wearables need to be designed so that people want to be seen wearing them for extended periods of time. A smartwatch or wireless pair of headphones must also be able to work seamlessly with other devices and services. A competitor needs to have not only an answer for effectively competing with Apple Watch on the wearables front, but also answers for various services available on AirPods and Apple’s other devices. Looking ahead, Apple’s entry into face wearables will only make the hill to climb that much steeper for competitors trying to go after Apple Watch and AirPods.
For competitors, the intimidating part is that the pieces needed to compete effectively with Apple wearables are unable to be worked on concurrently (at the same time). A company needs to first spend the required years developing and researching the core technologies before turning its focus on ensuring the right kind of collaboration exists between engineering and design. Product sales will then need to materialize before a company has the means of leaning on an ecosystem to sell additional wearable devices.
Apple M&A
A different way of measuring Apple’s lead in wearables is to look at the company’s M&A activity. Apple has been busy buying tech and talent for its upcoming face wearables play for the past six years. In wearables land, the days of new products taking only two to three years to develop are over. The required technology and R&D required to get such devices off the ground require much more lead time.
Metaio - AR (2015)
SensoMotoric Instruments – AR glasses (2017)
Vrvana – AR / hand & positional tracking technology (2017)
Akonia Holographics – AR glasses (2018)
NextVR – content platform for wearables (2020)
Spaces – content platform for wearables (2020)
Examples of Apple’s Lead
There are a number of real-world examples demonstrating Apple’s significant lead in wearables.
AssistiveTouch vs. Facebook Reality Labs. Two months ago, Facebook gave the press a peek at how it is researching using a smartwatch-like device as an input method for a pair of AR glasses. The research, centered on electromyography, looked to be in the pretty early stages with many years needed before seeing the technology in a consumer-facing product. The video was intriguing as it showed research that was thought to be at the forefront of what is going on in technology R&D today. Apple then shocked everyone by unveiling AssistiveTouch for Apple Watch. Instead of showing a behind-the-scenes look at an R&D project, Apple unveiled a technology ready for users today. The technology, relying on a combination of sensors and technologies to turn the Apple Watch into a hand / finger gesture reader, was designed for those in need of additional accessibility. Of course, the technology can go on to have other use cases over time, such as controlling a pair of smart glasses like the ones Facebook is working on. AssistiveTouch does a good job of showing just how far ahead Apple is on the wearables R&D front.
Google I/O 2021. At its 2021 developers conference, Google showed signs of finally taking wrist wearables seriously by ditching Wear OS and partnering with Samsung on a new OS. While it is fair to be skeptical that the effort will end up being successful, the announcement was a marked change from prior Google I/Os when wearables were all but ignored. Diving a bit deeper into Google’s announcement, it’s easy to see how far behind Google truly is in wearables. The company doesn’t even have an OS capable of powering a smartwatch. This may be excusable if Apple Watch was just unveiled. However, last month marked Apple Watch’s sixth anniversary.
Snap Spectacles 4 / Microsoft HoloLens / Magic Leap. While we see a handful of companies release various kinds of prototype hardware for the face (AR/VR/mixed reality), nothing has stuck with consumers. The feeling in the air is that they all lack something – design thinking. This is an item that is not easy to recreate with most companies simply not structured to emphasis design. Many companies will need to rethink their face wearables strategies once Apple enters the market. None have viable answers for smartwatches or wireless headphones either, which make their face-focused efforts look incomplete.
How Did This Happen?
Apple’s lead in wearables wasn’t driven by any one factor or item. Instead, a series of events came together to give Apple an advantage.
Apple was early. One way to build a big lead against the competition is to get an early start. Wearables represent a paradigm shift in computing, and few companies other than Apple saw it coming. As for how Apple was able to see it so early, wearables are all about making technology more personal - a mission Apple has been on for decades. In a way, Apple was built to excel with wearables. Apple’s lack of fear in coming up with new products that may potentially impact sales of existing products also helped the company run wrist-first into wearables in the early 2010s.
Voice computing distraction. Even after Apple began to unveil its wearables strategy, many competitors balked at following the company. Competitors thought the actual paradigm shift materializing was found with voice computing. Most of these companies didn’t have the hardware expertise to do well with wearables out of the gate, so they pinned their hopes on voice assistants being piped through stationary speakers. Once the stationary smart speaker mirage became apparent, companies found themselves years behind Apple on the wearables front.
Wearables require design expertise. It’s not enough to just throw together some leftover smartphone components and ship wearables. People want to wear devices that they are OK with being seen in. This is one reason why so many companies have looked at Apple Watch for design cues. The lack of design talent and ability remains a major roadblock for many companies.
Ecosystem and technology advantage. Wearables are the ultimate ecosystem play. On the technology front, Apple was able to utilize lessons learned from mobile devices to push wearables forward. Not many companies are able to do the same. Consolidation in the smartphone space has left only a handful of companies even in a position to have a wearables and mobile ecosystem. The probability of there being a wave of smartwatch OEMs utilizing something akin to Android remains low.
No price and feature umbrellas under Apple. One reason Android found oxygen in the smartphone space is that Apple left a pretty wide price umbrella under the iPhone. In addition, Android positioned itself as giving users features that iPhone users may not have had access to. No such umbrellas exist in wearables. Entry-level AirPods sell for $159 and are often available for less at third-party retailers. Apple Watch is available starting at $199. It is very difficult for a hardware manufacturer to sell wearables for less than Apple and turn a profit. Meanwhile, companies that would look to make money in other ways, such as through data collection, are still stuck with the requirement of wearables needing to look good enough to be worn in public.
Six years after releasing the Apple Watch, it’s still not clear who is going to represent genuine competition for Apple in the wearables space. Apple’s success in wearables is finally being noticed by others, as seen by the growing number of companies selling products for the body (Amazon, Microsoft, Facebook, Google, Samsung, Huawei, Xiaomi, Garmin, and the list goes on). However, none are in as strong of a position as Apple was in a few years ago, let alone today. Apple’s wearables lead stands to grow further once the company enters face wearables. The next few years will likely dictate the power structure in wearables for the next 10 to 20 years. When it comes to competitors figuring out a way to slow Apple in wearables, it’s now or never.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (3 stories per day, 12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
Apple's Ecosystem Growth Is Accelerating
The two most recent Above Avalon articles took a look at how and why Apple’s ecosystem is giving the company a major advantage against the competition.
With Apple reporting 3Q20 earnings two weeks ago, there is value in quantifying how much Apple’s ecosystem is growing. The data should startle the competition. Apple is seeing a clear acceleration in its ecosystem growth as hundreds of millions of iPhone-only users move deeper into the Apple fold by subscribing to various services and buying additional products.
Measuring Ecosystem Growth
There are a number of ways one can attempt to track or measure Apple’s ecosystem growth.
Number of devices per user
Number of paid subscriptions per user
In covering Apple’s business from a financial perspective, my modeling work includes keeping up-to-date estimates for most of the preceding data points. However, there is one metric missing from the list that may come as a surprise: overall revenue. Considering Apple provides this data point every three months, such an exclusion may seem peculiar. Wouldn’t Apple revenue shed light on how the Apple ecosystem is performing?
Relying on overall revenue for analyzing Apple’s ecosystem growth will lead to faulty conclusions. In Exhibit 1, Apple’s revenue is graphed on a trailing twelve months (TTM) basis. This is done to smooth out the seasonality found in Apple’s business (i.e. sales are concentrated around the holidays). The takeaway from the exhibit is that higher revenue demonstrates Apple’s ecosystem continues to grow although the rate of growth has slowed dramatically.
There is one problem with such a takeaway: It’s wrong.
Exhibit 1: Apple Revenue (TTM)
Click / tap exhibit to enlarge.
Overall revenue trends are masking what is actually occurring with Apple’s ecosystem. In FY2019, the iPhone was responsible for 55% of Apple’s overall revenue. On its own, that’s not an issue for Apple. The iPhone is part of Apple’s ecosystem after all. However, Apple has become increasingly dependent on existing users upgrading their devices to generate iPhone revenue. This has resulted in Apple’s overall revenue being heavily influenced by iPhone upgrading trends.
During periods of robust iPhone upgrading, Apple’s overall revenue shows stronger growth. When iPhone upgrading slows, overall revenue growth also slows to the point that Apple’s ecosystem may appear to be plateauing or even contracting (as seen in Exhibit 1). This was a major issue at the end of 2018 and early 2019 as slowing iPhone upgrades led many to conclude that Apple was in big trouble in China and other geographies.
Since iPhone upgrading trends have little to no direct impact on Apple ecosystem viability or strength, a better approach to get insights on Apple’s ecosystem growth is to divide Apple’s revenue into two categories:
iPhone
non-iPhone (Services, Mac, iPad, Wearables, Home, and Accessories)
As seen in Exhibit 2, breaking Apple’s overall revenue into iPhone and non-iPhone revenue leads to a completely different view of Apple’s growth trajectory. Non-iPhone revenue (the red line) continues to demonstrate very strong momentum while iPhone revenue (the blue line) is trending at the same level that it was in 2015.
Exhibit 2: Revenue (iPhone vs. Non-iPhone) - TTM
Click / tap exhibit to enlarge.
A different way of looking at this data is to consider revenue growth rates. Using the revenue figures from Exhibit 2, we are able to create Exhibit 3, which displays year-over-year change in revenue for both iPhone and non-iPhone.
Non-iPhone revenue growth (the red line) has outpaced iPhone revenue growth (the blue line) for the past seven quarters. The higher growth rates for iPhone revenue in 2018 were due to higher iPhone ASPs caused by Apple unveiling the iPhone X. Excluding those quarters, non-iPhone revenue growth has been trending stronger than iPhone growth since 2016. This is a sign that Apple’s underlying ecosystem strength has been gaining momentum for years - it’s just been masked by people holding on to their iPhones for longer before upgrading.
Exhibit 3: Revenue Growth YOY (iPhone vs. Non-iPhone) - TTM
Click / tap exhibit to enlarge.
What is driving the non-iPhone revenue strength shown in Exhibits 2 and 3? The answer is found in the strong iPhone revenue trends from a few years ago. Years of strong new user growth driven by the iPhone is now contributing to hundreds of millions of iPhone-only users moving deeper into the Apple ecosystem. This trend began in earnest around the beginning of 2017.
The Services Myth
Some may look at the preceding exhibits and say that the data is still incomplete. Apple Services include a number of recurring revenue streams such as iCloud, Apple Music, and various paid subscriptions. Given the recurring nature of something like paid iCloud storage, it ends up being easier for Apple to report year-over-year Services growth. Apple’s Services business accounts for 40% of non-iPhone revenue. There is a different dynamic found with hardware revenue. Since hardware isn’t a recurring revenue stream, year-over-year growth ends up being that much harder to achieve as Apple is in effect needing to replace every dollar of revenue with new sales.
(One can argue something like the iPhone Upgrade Program is a recurring revenue stream for hardware. However, that ends up being a stretch. The Upgrade Program is a loan with a built-in upgrade optionality after the 12th payment. That is very different than something like an iCloud or Apple Music subscription.)
To address this issue, non-iPhone revenue can be broken out into Services and Products (excluding iPhone). In what will come as a shock to many people, Exhibits 4 and 5 show how Products revenue excluding iPhone (i.e. iPad, Mac, Wearables, Home, and Accessories) is now growing at nearly the same pace as Services. This represents a major narrative violation as consensus spent years positioning Services as Apple’s growth engine.
Exhibit 4: Revenue (Apple Services vs. Apple Products Excluding iPhone) - TTM
Click / tap exhibit to enlarge.
Exhibit 5: Revenue Growth YOY (Apple Services vs. Apple Products Excluding iPhone) - TTM
Click / tap exhibit to enlarge.
Based on Apple management commentary, we know that upgrading is not impacting the iPad, Mac, and wearables as much as the iPhone. Approximately half of people buying iPads and Macs are new to the product categories. For Apple Watch, the percentage is more than 75%. The new user percentage for iPhone sales is a fraction of those percentages. This tells us that iPad, Mac, and wearables sales are a very good indicator of Apple ecosystem strength.
Tying It All Together
One way of thinking about the Apple ecosystem is to view it as a pie. There are two ways for Apple to expand the pie: Bring in more customers and have existing customers spend more on services and products in the ecosystem (higher ARPU).
New users entering the ecosystem - The iPhone SE should not be underestimated as a successful tool for bringing Android users into the Apple fold.
Existing users moving deeper into the ecosystem - iPhone users are buying iPads, Macs, and wearables as well as subscribing to various Apple services.
Apple currently finds itself in an ecosystem expansion phase. Hundreds of millions of people with only one Apple device - an iPhone - are embarking on a search for more Apple experiences. We see this with non-iPhone revenue growing by 14% in 3Q20 on a TTM basis, which is higher than growth rates seen in the mid-2010s, as seen in Exhibit 6.
Exhibit 6: Apple Non-iPhone Revenue Growth Projection
Click / tap exhibit to enlarge.
Looking ahead, my estimates have non-iPhone revenue accelerating from 14% growth to 20% growth in the coming quarters. iPad, Mac, and wearables are a major source of that growth acceleration. Considering how Apple is working off of a much larger revenue base, for revenue growth percentages to actually increase this far along in the process is intriguing. The takeaway is that Apple’s ecosystem is gaining momentum at a pace that should frighten the competition.
Hundreds of millions of people will be buying their first Apple wearable device in the coming years. Given the inherent nature of wearable devices - new form factors designed to make technology more personal - it is very likely that one Apple wearable purchase will eventually lead to additional Apple wearable purchases. Apple can then leverage high-margin Services to run with more aggressive pricing on wearables (and other Apple devices) which only ends up boosting demand.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members in both written and audio forms. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
For additional discussion on this topic, check out the Above Avalon daily update from August 13th.
The Secret to Apple's Ecosystem
Apple’s ecosystem remains misunderstood. While consensus has come around to accepting the sheer size of Apple’s ecosystem (a billion users and nearly 1.6 billion devices), there is still much unknown as to what makes the ecosystem tick. From what does Apple’s ecosystem derive its power? Why do loyalty and satisfaction rates increase as customers move deeper into the ecosystem? Apple’s ecosystem ends up being about more than just a collection of devices or services. Apple has been quietly building something much larger, and it’s still flying under the radar.
Products
No company is able to match Apple in offering a cohesive and strategically forward-looking product line. Computers small and light enough to be worn on the body are sold next to computers so large that built-in handles are required. More impressively, all of these products are designed to work seamlessly together.
The Grand Unified Theory of Apple Products outlines how each of Apple’s major product categories is designed to help make technology more personal - to reduce the barriers that exist between technology and the user.
Products are designed to handle tasks once handled by more powerful siblings. New form factors are then able to handle new tasks in unique and different ways. It is the pursuit of making technology more personal that ends up being responsible for devices like Apple Watch and AirPods. The same dynamic is also paving the way for Apple to eventually sell wearables for the face in the form of smart glasses. (More on The Grand Unified Theory of Apple Products is found in the Above Avalon Report, “Product Vision: How Apple Thinks About the World,” available here for Above Avalon members.)
With 1.6 billion devices in use, it may be natural to conclude that devices are the source of Apple’s ecosystem power. This has led some to position the iPhone as the sun in Apple’s ecosystem with other products being the planets revolving around the sun. However, this is a misread of the role Apple devices are actually playing in the ecosystem. Just because the iPhone is used by more people than any other Apple device, it is incorrect to assume that will always be the case, or more importantly, that other devices are in some way inferior to the iPhone when it comes to handling workflows. There is something much larger at play here than just a billion users enjoying Apple hardware.
Services
With a $55 billion revenue annual run rate and 518 million paid subscriptions across its platforms, there is no longer a debate as to Apple’s ability to succeed with services. However, there is still a lack of consensus as to what role services play in Apple’s ecosystem. Decisions like bringing Apple Music to third-party speakers and the Apple TV app to third-party TV sets have confused many with some going so far as to conclude that Apple’s future is one of a services company.
In such a world, Apple devices lose much of their value to cheap third-party hardware. This school of thought is responsible for claims that Apple gave up selling accessories like the Apple TV box and HomePod because customers can access Apple content distribution services on cheaper non-Apple hardware. It’s difficult to think of a bigger misread of how Apple thinks and operates as a company than to claim that Apple’s future is one of a services company.
There are now others who look at Apple’s financial success with services as a negative - a sign of Apple milking existing users of as much profit as possible. This school of thought positions paid services as a long-term liability to the Apple ecosystem.
A Toolmaker
While consensus credits products (hardware) as the source of Apple’s ecosystem power, services are increasingly viewed as a hidden risk factor that can crack holes in the ecosystem. Neither are true. Nearly a billion people are not using iPhones simply because they enjoy the hardware. Vice-versa, having 518 million paid subscriptions is not a sign of Apple users needing to pay some kind of tax or bounty to remain in Apple’s ecosystem.
From where then does Apple’s ecosystem derive its power? What makes a customer want to move deeper into the Apple ecosystem?
To answer these questions, we need to step back from any one product or service and instead look at Apple as a company. It is still common for people to call Apple by whatever is its best-selling or most popular product at any one time. This also applies to whatever product is responsible for revenue growth. As a result, we hear all too often phrases like Apple is an iPhone company, a services company, or even a wearables company. The problem is that Apple shouldn’t be defined by any one product, but rather the process that led to Apple having an ecosystem of products and services.
Apple is a design company selling tools that can improve people’s lives. These aren’t just any tools either. Instead, Apple is very selective in selling tools that are able to foster experiences that people are willing to pay for - something that has become increasingly rare in the consumer tech space. By having a design-led culture, Apple is able to put the user experience front-and-center during product development.
This experiences mandate ends up being responsible for Apple’s high loyalty and satisfaction rates. The 975 million people with an iPhone aren’t likely to remain iPhone users because of stellar hardware or compelling software powering that hardware. Instead, loyalty is driven by the experiences associated with using an iPhone.
An Experiences Ecosystem
The secret to Apple’s ecosystem is that instead of selling products or services, Apple ends up selling experiences made possible by controlling hardware, software, and services.
Instead of thinking of Apple’s ecosystem in terms of the number of people or devices, a different approach is to consider the number of experiences Apple is offering. This is where Apple’s true ambitions become visible. By using an iPhone, a customer doesn’t just receive one experience per day. Instead, nearly everything that is consumed on the device has the potential of leading to a good (or bad) experience. This is why Apple’s control of hardware, software, and services plays such a crucial role. Apple’s ecosystem likely consists of tens, if not hundreds of billions, of experiences in a single day.
Having an ecosystem of experiences ultimately represents the biggest challenge to Apple competitors. Coming up with an iPhone alternative isn’t good enough for enticing users to jump from the Apple ship. Instead, competitors need to come up with even better experiences than those found in the Apple ecosystem. As a user moves deeper into the Apple ecosystem - in pursuit of additional premium experiences - competitors need to figure out a way of recreating that growing list of experiences. Can it even be done? When looking at the wearables industry, the answer as of today is “no.”
Non-Apple Hardware
One of the most intriguing aspects of Apple’s ecosystem is how nearly half of Apple users still only use just one Apple device: an iPhone. The idea that every Apple user owns a multitude of Apple devices and services is wrong. The implication is that Apple’s billion users own (and use) quite a bit of non-Apple hardware. Today, non-Apple hardware used by iPhone owners include TV sets, cheap stationary speakers, and CarPlay-equipped automobiles.
Since Apple’s product strategy and organizational structure rewards saying “no” more than “yes,” there will likely always be opportunities for other companies selling hardware to participate in the Apple ecosystem. This ends up being a Trojan Horse for Apple.
Instead of needing to have a new customer jump with both feet into the Apple ecosystem from Day 1, something that isn’t likely especially as the next marginal customer will be coming from the middle tier of the market, Apple merely needs this customer to buy or use one Apple tool.
Management is confident that one tool will eventually turn into two tools and then three since humans gravitate toward premium experiences. As one’s Apple tool collection grows, the number of experiences made possible by those tools increases. This has the impact of increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. And the flywheel continues to turn. In order to get this flywheel moving in the first place, Apple must build bridges allowing new customers to move deeper into the ecosystem. Decisions like making Apple Music available on non-Apple hardware and bringing the Apple TV app to Samsung TVs are examples of such bridges.
Evolution
When thinking about how Apple’s ecosystem will evolve, the focus shouldn’t be on which new devices or services Apple can come up with, but rather on how Apple can offer new experiences to its customers. The blueprint for creating such experiences is already known: leveraging control over hardware, software, and services.
Technology’s battle lines are currently being redrawn with the goal being to capture the most valuable real estate in our lives: our health, homes, and transportation. Bets on software that completely reimagines the way we approach these verticals will likely prove to be good bets. Timing remains the big unknown.
This raises a question: How will Apple approach new verticals and industries? Would Apple attempt to recreate entirely new device lineups for each industry? Will The Grand Unified Theory of Apple Products be torn apart?
Instead of selling a $80,000 electric car or moving head-first into selling a range of first-party smart home hardware, Apple’s current ecosystem provides clues as to how the company can approach these new industries.
The point of Apple entering transportation wouldn’t be to sell cars, mopeds, or bicycles. Instead, it would be to sell experiences that Apple customers can consume on the road.
The point of Apple moving deeper into smart homes wouldn’t be to sell a plethora of small home gadgets and trinkets, some of which may require an electrician to install. Instead, it would be to sell experiences that Apple customers can consume in the home.
Apple developing an autonomous car remains difficult for many to wrap their minds around. The idea of Apple one day getting into housing is still considered a fantasy by most. However, such ideas make a lot of sense when thinking about how we consume experiences during the day.
An autonomous car is nothing more than a room on wheels. A house is a series of rooms connected to each other. With each, Apple would be looking to create environments that can support new experiences.
This brings us back to Apple’s current suite of products and services. It is incorrect to assume that Apple entering new industries would result in the company throwing its current products out the window. Instead, those tools stand to play major roles in delivering experiences in new industries.
Apple’s interest with Project Titan isn’t to beat or copy Tesla, but rather to figure out a way to have personal gadgets provide compelling experiences on the road. Such experiences could include Apple Glasses being used to find the right autonomous Apple Car to enter while Apple Watches can be used as identification for entry. Once inside the vehicle, the digital assistant found on the wrist or in front of our eyes could then be used to convert the car’s hardware to suit our needs. A similar dynamic would be found with smart homes - relying on personal gadgets, especially wearables, to come up with premium experiences in the home. We are seeing the early stages of this with products like HomePod and the way the device can be seamlessly used with Apple Watch.
The idea that Apple would enter the transportation and housing industries simply to come up with more areas for its users to engage with wearables may seem preposterous today. However, the idea that a single company would be able to deliver hundreds of billions of experiences per day by selling tools consisting of hardware, software, and services was similarly once a fantasy.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members in both written and audio forms. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
For additional discussion on this topic, check out the Above Avalon daily update from July 23rd.
Apple Is Pulling Away From the Competition
For the second year in a row, Apple held a developers conference that should frighten its competitors. Relying on a nearly maniacal obsession with the user experience, Apple is removing oxygen from every market that it plays in. At the same time, the tech landscape is riddled with increasingly bad bets, indifference, and a lack of vision. Apple is pulling away from the competition to a degree that we haven’t ever seen before. Given how we are just now entering the wearables era, implications of this shift will be measured in the coming decades, not years.
WWDC 2020
It speaks volumes that Apple held its strongest WWDC in years during the middle of a pandemic while two of its largest competitors, Google and Facebook, decided to skip their annual developers conferences. Just a few years ago, fortunes were reversed. Apple was coming under fire for WWDCs that appeared to be more reactionary to Google, Facebook, and Samsung. Apple was also struggling to contain growing unrest among its pro users who were tempted by Microsoft Surface hardware.
What changed?
The last two WWDCs stood out for two reasons:
A revised Apple product strategy. A few years ago, Apple was most aggressive with products capable of making technology more relevant and personal (iPhone and Apple Watch). As shown in Exhibit 1, in the pull strategy, the Apple Watch and iPhone were Apple’s clear priorities while the iPad, Mac portables, and Mac desktops ended up facing a battle for management attention as if they were located at the end of the rope that was Apple management was pulling.
Apple changed from a “pull” strategy in which some products like the iPad and Mac seemed to be having a hard time keeping up to a push strategy characterized by every major product category moving forward simultaneously. This shift appears to have been born in 2017, which would explain why we are still seeing the initial fruit of the effort. The iPad and Mac product categories have benefited the most from this revised “push” product strategy with more frequent and noteworthy updates.
Exhibit 1: Apple’s Changing Product Strategy
Apple has doubled down on its unique interpretation of innovation. During his opening remarks at the iPhone and Apple Watch event last September, Tim Cook said that Apple sells tools containing "[i]nnovations that enrich people's lives to help them learn, create, work, play, share, and stay healthy." Instead of defining innovation as either being first or doing something different, Apple looks at innovation as something that improves customers’ lives. A major consequence of this has been software and hardware releases that have prioritized feature quality over quantity. This year’s WWDC came in a full 20% shorter than previous keynotes. While having a digital format helped cut down on the timing due to quicker transitions, no clapping etc., there were also fewer new features announced. However, the features that were announced contained more significance when it comes to pushing the user experience forward.
A Stronger Apple
Unfortunately for Apple competitors, the combination of a revised product strategy and unique definition of innovation didn’t just make for strong WWDC keynotes. Consumers are noticing and wanting what Apple is selling. Consider the following trends:
Apple hasn’t just held its own in the smartphone space but rather is continuing to take share from Android. Of all the smartphone manufacturers, Apple saw the largest sales share increase in the smartphone industry last quarter, and that was during a pandemic.
Apple is adding approximately 20 million new iPad users per year despite the iPad being 10 years old and already having an installed base exceeding 300 million users.
Apple’s oldest major product category, the Mac, is adding 10 million new users per year.
Apple Watch and AirPods are quickly approaching 100 million user bases each.
Apple users are paying for 518 million subscriptions across Apple’s platforms, which is up 126 million in just a year.
All of the preceding items amount to an Apple ecosystem gaining momentum. A different way of highlighting Apple’s growing ecosystem over the past 10 years is to look at the number of people using at least one Apple device. As shown in Exhibit 2, Apple’s installed base recently surpassed a billion users.
Exhibit 2: Apple Installed Base (Number of Users)
While new user growth rates have slowed, Apple is still bringing tens of millions of users into the fold. Due to Apple’s views regarding innovation and its focus on the user experience, once someone enters the Apple ecosystem, odds are good that customer will remain in the ecosystem.
This is why one subtheme from last week’s WWDC keynote flew under the radar. (My complete WWDC 2020 review is available here for Above Avalon members.) It’s not just about Apple pushing multiple product categories forward at the same time. Instead, it’s about adding cohesiveness and commonality between product categories. Apple is making it easier for people to buy multiple Apple devices. As users move deeper into the Apple ecosystem, satisfaction and loyalty rates stand to go even higher. The end result is that Apple’s billion users aren’t just any billion users. Instead, they are a billion users less likely to use non-Apple devices and services going forward. For the competition, this is a highly concerning development.
More worrying for competitors, Apple is still in the early stages of bringing its users deeper into the ecosystem. According to my estimate, approximately 50% of Apple users still own just one Apple device: an iPhone. This group serves as a prime market for products like the iPad, Apple Watch, AirPods, and various Apple services. In a few years, that percentage may decline to something more like 30%. Such a development will remove much of the remaining oxygen from the markets Apple plays in.
Competition Is Weakening
While Apple sails forward with a strengthening ecosystem made possible by a clear product vision and a functioning organizational structure that prioritizes design (i.e. the user experience), the competition is rudderless.
Apple competitors have been striking out with one bad product bet after another. Few have long-term vision as to where computing is headed. Consider the following events, developments, and observations. By no means is this an inclusive list.
Samsung remains rudderless from a product vision perspective. With no clear direction as to where to go, the company aimlessly launches new products and features for no other reason than to say they are first. The strategy is no different than throwing things against the wall and hoping something sticks. Even worse, the products and features that Samsung is announcing aren’t even ready for public usage.
Google continues to prioritize technology over design. While new software features may seem compelling on paper, the lack of attention given to the user experience quickly becomes apparent. It has also become difficult to miss the growing enthusiasm gap between Android and iOS. On the hardware front, Google is struggling to match such efforts with its ambient computing future (which doesn’t make much sense to me).
Amazon’s massive bet on voice with Alexa and Echo was the wrong one. The stationary smart speaker space was a mirage. Amazon should have instead bet on wearables with voice as a user input. However, the company doesn’t have the corporate culture to excel with computers worn on the body.
Microsoft appears to be running into growing trouble with the consumer when it comes to Surface. What had been a genuine chance to rip into the iPad and Mac stronghold due to growing user unrest looks to have been successfully crushed by Apple. Microsoft Surface revenue is increasingly being driven by commercial clients (i.e. Microsoft is taking share from its OEMs rather than Apple).
Facebook ended up placing the wrong social bet. Instead of going after our closest social network, Facebook evolved to offer a curated version of the web via the News Feed. The company’s pivot back to a privacy-focused social platform built around messaging emphasizes this wrong bet. A message sent through Apple’s Messages is a message not sent through a Facebook property.
Snap, the company considered to have the best odds of competing with Apple on AR, botched its first major foray into AR hardware with Spectacles. The company has backed itself in a corner by management’s refusal, and then failure, to appeal to older demographics. This will serve as a headwind for mass market AR successes.
Spotify was not able to prevent Apple Music from gaining critical mass despite Apple Music not having a free tier. The same is now taking place with Netflix, which is unable to stop new entrants into paid video streaming from gaining traction. This ends up diffusing near universal praise in the press for first movers.
For an industry that was expected to put Apple in its place, that sure is a lot of fails, flops, and disappointments. When looking outside the U.S., the overall picture isn’t dramatically different. While some companies still have pockets of strength where Apple is not a major player, in geographies Apple is playing in, the company continues to see growing ecosystem momentum while the competition flounders. The number of paid subscriptions being run through Apple’s platform points to increased services and app adoption outside the U.S.
The never-ending tales of Apple being crushed by the local competition in China have been met with Apple seeing existing users move deeper into the ecosystem as measured by App Store, iPad, and wearables momentum. Huawei’s struggles in Europe appear to be benefiting Apple at the premium end of the market.
Changing Narrative
If there was still doubt about Apple’s momentum in the marketplace, one doesn’t need to look any further than the dramatic change in narrative facing Apple in the press.
For years, Apple was positioned as one iPhone update away from implosion. Low market and sales share were paraded around as signs of an incompetent product strategy. Simply put, Apple was framed as being weak and vulnerable, dependent on revenue sources that could disappear overnight due to consumers fleeing to the competition.
The narrative has completely shifted. The press is now infatuated with Apple’s power, its ironclad grip over the App Store, and the idea that Apple users are stuck or imprisoned in a massive walled garden where things like iMessage, Apple Watches, and AirPods force people to remain within Apple’s walls. Government regulators are viewed as the only entity capable of protecting Apple users from Apple.
If competitors actually believe this narrative, they are setting themselves for more failure. Thinking that Apple users are somehow being forced against their will to buy products like Apple Watches and AirPods is nothing more than looking for someone to blame for market failures when the problem is found internally with a bad vision, inadequate corporate culture, and lack of understanding as to what makes Apple unique.
Risks
On a list of risk factors facing Apple, greater regulation is far from the top. The same can be said about things like App Store policies and employee retention. While these items make for juicy headlines capable of grabbing people’s attention, they won’t play a major role in Apple’s future. Instead, Apple is where it is today by saying “no” more than “yes.” By remaining focused on making technology more personal, which is inherently about using a design-led culture to push the user experience, Apple is able to develop a dynamic, yet nimble, ecosystem of tools that people are willing to pay for. lf it were to lose focus, Apple would move that much closer to its competitors.
Apple ends up being its toughest competitor as it releases products that surpass the previous version. This is where betting on the user experience and taking a unique stance on innovation is critical.
Next Ten Years
When the iPhone was unveiled in 2007, Steve Jobs claimed that Apple had a five-year head start against the competition. He ended up being mostly right. By 2012, Samsung and Google were shipping credible iPhone alternatives, thanks partially to ruthless copying that led to time in the courtroom.
With wearables, my thinking has been that Apple has a lead that is closer to 10 years. This estimate reflects not just software or hardware advantages, but also the byproduct of Apple controlling both items and its resulting achievements with custom silicon.
As time passes, Apple has been facing less competition in wearables. This is remarkable considering how Apple Watch has already ushered in the next paradigm shift in computing. We are seeing the future today. Yet most companies either don’t see it or even worse, see it but are unable to respond.
Giving Apple a 10-year head start against the competition with wearables may end up giving too much credit to the competition. Excelling in wearables requires a corporate culture, product development process, and business model that few companies other than Apple possess. In many ways, Apple was built to excel in wearables. Apple should probably get used to being its own toughest competitor.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
AirPods Are Becoming a Platform
If AirPods were magical, AirPods Pro are supernatural. Apple’s newest pair of AirPods continues to make waves with “augmented hearing” entering people’s vocabulary. However, the broader implications found with Apple’s AirPods strategy are just as impressive. Apple is quickly removing all available oxygen from the wireless headphone market, and competitors find themselves at a severe disadvantage. In just three years, AirPods have evolved from an iPhone accessory into the early stages of a platform well positioned to reshape the current app paradigm for the wearables era.
Another “Quiet” Launch
One of the more fascinating aspects found with AirPods Pro was how the product was unveiled. Instead of receiving stage time at Apple’s big product event at Steve Jobs Theater one month earlier, AirPods Pro received the press release treatment. When contemplating potential sales, AirPods Pro may end up being the best-selling Apple product that has ever been unveiled with just a press release.
The subdued unveiling given to AirPods Pro is consistent with Apple’s prior approach to AirPods. Instead of receiving the red carpet treatment as the Apple Watch did two years earlier, AirPods were unveiled to the world over the course of just five minutes at Apple’s iPhone and Apple Watch event at Bill Graham Civic Auditorium in San Francisco. In a sign of just how nonchalant Apple was with the unveiling, AirPods were positioned merely as an iPhone 7 and 7 Plus feature. The product was said to be an additional option that consumers had for handling the transition away from dedicated headphone jacks. (Remember those?)
Earlier this year, AirPods with wireless charging case was unveiled via press release as well.
AirPods Pro
It’s easy to gloss over many of the selling points found with AirPods Pro given the familiarity with AirPods. Items such as seamless pairing and the carrying case that doubles as a charging station play crucial roles in giving AirPods Pro such a high-quality and enjoyable user experience.
However, the features that have gained the most attention, and rightly so, are Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) and Transparency mode. For many people, AirPods Pro will be their first pair of ANC headphones. Those users are in for a treat as Transparency mode addresses the largest negative found with ANC headphones - the user is seemingly removed from his or her surroundings. A press and hold on one AirPod stem switches between ANC and Transparency mode. The functionality is a great example of how Apple’s engineering and design teams, through collaboration, can produce a great user experience.
Sales
In FY2019, Apple sold 35 million pairs of AirPods at an average selling price (ASP) of $162 (both are my estimates). On a revenue basis, the AirPods business is on a $6 billion per year run rate that is doubling year-over-year.
One way to put those sales numbers into context is to compare AirPods to other Apple products at the same point in time after launch. As shown in Exhibit 1, AirPods are trending similarly to iPhone sales when looking at unit sales out of the gate. After three years of sales, Apple has sold 61 million pairs of AirPods on a cumulative basis. During the first three years of sales, Apple sold 60 million iPhones.
Exhibit 1: Unit Sales out of the Gate
Apple likely crossed an important AirPods sales milestone last quarter. For the first time, Apple sold more than 10 million pairs of AirPods during a three-month stretch. While the preceding observation came from my earnings model (access to my Apple earnings model is a benefit associated with Above Avalon membership at no additional cost), the math checks out with Apple management’s commentary and clues provided on the 4Q19 earnings conference call. It’s likely that AirPods sales will exceed 10 million per quarter for the foreseeable future.
When contemplating AirPods unit sales trends going forward, too many people are stuck in a mobile mindset. Instead of seeing someone buy and use just one pair of AirPods, we may see a new kind of usage pattern develop in which a growing percentage of AirPods owners will use more than one pair of AirPods. This will help boost AirPods unit sales.
On Apple’s 4Q19 earnings conference call, Tim Cook was asked about the potential upgrade trajectory for AirPods. Cook commented that he thought current AirPods owners would be in the market for AirPods Pro to “have a pair for the times that they need noise cancellation.” The clear implication found in Cook’s comment was that Apple expects some AirPods owners to use multiple pairs of AirPods with differing levels of functionality.
After just three years of sales, we are already starting to see the early stages of this trend develop with people upgrading their AirPods but keeping their old pair as a backup.
In an unscientific poll conducted via Twitter poll through my account, 30% of respondents said they use more than one pair of AirPods. Interestingly, 41% of people who said they purchased a pair of AirPods with wireless charging case claim to still be using their older pair of AirPods as well. It helps that AirPods last years before poor battery life takes its toll. My initial pair of AirPods from 2016 are still used daily. It's early, but it looks like people using more than one pair of AirPods is a thing.
Platform Building
The current app paradigm primarily consists of downloading an app to our smartphone, tablet, smartwatch, smart TV, or laptop / desktop. We then interact with the app to “pull” information and context at a time of our choosing. App notifications are not very smart and instead represent mostly useless distractions more than anything else.
The Apple Watch was the first device to genuinely begin questioning the current app paradigm. The Siri watch face on Apple Watch is all about providing the wearer glanceable amounts of information, data, and context in the form of cards chosen by a digital assistant. These cards are personalized to the wearer based on the time of day and schedule. In essence, we are moving away from pulling data from various apps to receiving a curated feed of data that is dynamic - always changing and tailored to our needs.
Apple is turning AirPods into the second platform built for what comes after the App Store. Instead of being about pushed snippets of information and data via a digital voice assistant, something that will likely remain ideal for mobile screens, AirPods will be all about augmenting our environment by pushing intelligent sound.
AirPods Pro wearers are able to experience the early days of this dynamic with Transparency mode. Switching between Transparency mode and ANC is equivalent to augmenting our environment. We are receiving two different experiences despite being in the same location.
This dynamic could be extended so that a simple tap of an AirPod or a quick voice command can take us to a different location via sound. Utilizing HomePods as sound receivers, an AirPods wearer would be able to “move” from the kitchen to family room. A quick tap of one AirPods, or Siri voice command could bring the wearer from the family room to kitchen to answer a family member’s question or simply to be “in” the room.
App developers would be able to take part in this revolution by building experiences that further augment people’s hearing. “Apps” would amount to tools capable of adding context to our hearing. Fitness can be rethought by adjusting the AirPods wearer’s hearing during workouts and exercise based on his or her activity. As an example, AirPods music playbook can be adjusted based on the users’ heart rate obtained by an Apple Watch. Such adjustment would amount to the AirPods wearer being “removed” from his or her environment when close to reaching a maximum heart rate during a run or track workout. Of course, such health tracking and monitoring may one day be brought directly to AirPods in subsequent editions.
Another example involves utilizing AirPods to deliver different sound experiences to different people despite being in the same location and looking at the same thing. As an example, a single presentation shown in a school or office setting can end up delivering a dozen different experiences to those in attendance.
Platform Power
AirPods will derive its platform power from three sources:
Technology advantage
Design focus
Massive adoption
Apple is pulling away from the competition when it comes to building mini computers worn on the body. AirPods are computers for the ears. Years of learning how to manufacture 2.1 billion iPhones and iPads is now helping Apple to build nearly 70 million wearable devices per year.
This technology prowess and manufacturing acumen goes to waste if people don’t actually want to be seen wearing the devices. Apple’s success at redefining luxury, combined with the company’s design-led culture, gives the company a large advantage in the area of understanding what people will want to wear on the body.
The final source of platform power will come from massive adoption. There are currently 45 million people wearing AirPods. At the current rate, more than 100 million people will be wearing AirPods at some point in 2021. As to how Apple is able to see such strong AirPods adoption, Apple is busy removing all available oxygen from the wireless headphone market.
The company is utilizing a masterful combination of price and features to establish multiple beachheads in the market.
AirPods Pro do not replace AirPods in the product line. Apple is instead embracing a strategy of expanding the product line according to functionality. AirPods Pro represent the expansion of the AirPods line into a higher-end segment that places value with ANC. The end result is that Apple now has three different AirPods model, each targeting a different price segment of the wireless headphone market. It is certainly reasonable to expect Apple to continue pushing this strategy in the coming years so that we see a pair of AirPods go for as low as $99 and as high as $500.
We see similar product strategies with the iPad and Mac lines. With these, Apple sells a range of flagship products with varying degrees of functionality, and of course, price.
There are some unique attributes seen in Apple’s campaign to remove oxygen from the wireless headphone market. Unlike what they did with the iPhone or iPad playbook, Apple didn’t launch AirPods at one price and then begin to lower pricing once all of the profit had been sucked from that initial market segment. Instead, Apple has been doing the opposite. Apple unveiled AirPods at a very aggressive $159 price, which sent shockwaves across the industry as the competition was priced closer to $300. Three years later, competitors are still struggling to match AirPods' $159 entry-level price.
Something Big
This AirPods evolution into a platform does not come as a surprise. Here was the opening paragraph from my initial Above Avalon article on AirPods shortly after being unveiled in September 2016:
“AirPods will turn out to be one of the more strategically important hardware products Apple has released this decade. However, you would never know it judging from the way Apple unveiled the device last week. I suspect that was intentional. While the press remains focused on the short-term debate surrounding the iPhone's lack of a 3.5mm headphone jack, few have realized that Apple just unveiled its second wearables platform.”
Three years later and that paragraph still rings true. AirPods have turned into a cultural phenomenon while dedicated headphone jacks on smartphones have become relics. Meanwhile, Apple’s wearables train continues to gain momentum as the company grabs real estate on our wrists and in our ears by bringing a new level of personal computing to the masses.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
Apple Deserves More Credit for Wearables
The wearables era at Apple began years ago. However, Wall Street and Silicon Valley are only now slowly starting to pay attention to what Apple has been building. Apple is the undisputed leader in wearables, and they are pulling away from the competition. Given how Apple’s wearables strength continues to be underestimated, the company deserves more credit for what it has achieved and where it is headed.
The Data
A takeaway from Apple’s recent 3Q19 earnings was that we are witnessing the wearables era continue to unfold at Apple. Segmenting Apple’s quarterly revenue growth into product categories is one way of highlighting wearables momentum. Both an accurate financial model and close following of Apple clues over the past four years are required to accurately estimate Apple Watch and AirPods unit sales and average selling prices (ASPs). Therefore, this exercise has not been practiced by many.
The preceding totals represent the change in revenue from 3Q18 to 3Q19.
Apple Revenue Growth Drivers (3Q19)
Services: $1.5 billion
Wearables: $1.2 billion
Home / Accessories: $0.6 billion
Mac: $0.6 billion
iPad: $0.4 billion
Note: These totals do not represent revenue totals but instead the change in revenue between 3Q18 and 3Q19.
The revelation from the preceding data is riveting. Wearables nearly exceeded Services in 3Q19 as Apple’s top revenue growth generator when looking at absolute dollars. Consensus was not expecting this to occur as Services was positioned as Apple’s growth engine. It is clear that consensus spent too much time on the Services highway and ended up missing the exit for wearables.
In taking a closer look at wearables revenue growth, it becomes evident that Apple is benefiting from both higher ASPs for Apple Watch and AirPods as well as continued strong unit sales growth. For AirPods, unit sales growth is nothing short of spectacular at 80%.
Speaking of unit sales, one out of five gadgets that Apple sells is now a wearables device. Exhibit 1 highlights the growing share that wearables represent when looking at overall Apple device unit sales.
Exhibit 1: Wearables Share of Apple Device Unit Sales
Exhibit 2 depicts wearables’ growing share of gadget sales relative to Apple’s other product categories. Apple is currently selling approximately 70M wearable devices per year. This includes 30 million Apple Watches and more than 30 million AirPods.
Exhibit 2: Apple Gadget Unit Sales
On a revenue basis, Apple’s wearables business is now at a $16 billion annual run rate growing at 55% to 60%. At the current pace, wearables will surpass both the iPad and Mac near the end of 2020 to become the third largest product category behind iPhone and Services when looking at revenue.
The Wearables Train
One way of thinking about Apple’s wearables business is that it’s a train gaining momentum. Competitors face declining odds of being able to stop the train.
The Apple wearables train is boosted by three items that no other company has the luxury of utilizing or leveraging:
A massive installed base of iPhone users (925M globally).
Core competencies and a company culture built on making technology more personal, intuitive, and easy to use.
A thriving platform of multiple wearables products.
Apple is leveraging its ecosystem of users and devices to give its wearables business an ideal launching pad for success. While there are handful of companies with more than a billion users, no other company has an ecosystem of a billion users and nearly 1.5 billion devices (nearly 90% of which are running the latest software). The lack of a self-sustaining ecosystem is one of the primary factors driving Fitbit’s gradual fade into irrelevancy. This limitation manifests itself in new products like the Fitbit Versa smartwatch failing to catch the needed traction.
Design, or the lack thereof, is proving to be another high barrier for many companies to get over in terms of wearables. Silicon Valley continues to focus too much on technology and not enough on design, or how we actually use technology. Google’s ineptitude when it comes to wearables is partially due to the company not having a clue as to how to get people to wear wearable devices. Management thought consumers would want to wear Pixel earbuds because the devices had real-time translation. In reality, consumers don’t want to be seen in public wearing wireless headphones that don’t reflect aspiration and coolness. A keen understanding of how to play in the luxury and fashion realms while simultaneously appealing to the mass market is tricky.
Flying Under the Radar
In assessing why Apple’s wearables business has received so little attention to date, one doesn’t have to look much further than the iPhone. Preoccupation with trying to find a singular product capable of replacing iPhone made it difficult for many to see how a platform of wearable devices is the answer for what can eventually serve as a viable iPhone alternative.
A cellular Apple Watch paired with AirPods is already able to handle a number of tasks currently given to the iPhone. Add a pair of smart glasses to the mix, and mobile devices like the iPhone and iPad stand to lose even more use cases.
It doesn’t help that new Apple products are also graded on a curve next to iPhone. If a new product is unable to move Apple’s financial meter out of the gate, the product is looked at as a flop, toy, or mere iPhone accessory.
Guardrails
For competitors, the bad news is that there is evidence that Apple is still applying some breaks to its wearables train. In some ways, Apple is holding things back. An iPhone is still required to set up an Apple Watch. A truly independent Apple Watch that doesn’t require an iPhone would grow the device’s addressable market by three times overnight.
In addition, Apple currently only offers wearables devices for two pieces of real estate on the body: our wrists and ears. A compelling argument can be made that the most prized piece of wearables real estate, our eyes, remains untapped.
Looking Ahead
We are witnessing wearables usher in a paradigm shift when it comes to how we use and interact with technology. Apple deserves more credit for not only choosing to ride the wearables wave, but also playing a crucial role in getting wearables off the ground.
Apple is well on its way to having Apple Watch and AirPods installed bases of 100M people each. The company is more than half way there with Apple Watch and is quickly approaching the same level with AirPods despite the product being sold for half the time.
Apple also finds itself in the midst of a major investment phase to expand its wearables platform. There is an opportunity to bring more utility, in addition to clearer vision, to the eyes in the form of smart glasses. Such a product would be a precursor to a pair of AR glasses.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.